Reflectivity Measurement
 |
 |
The device shown in Fig. 15 consists of a laser and detector mounted on a support structure that can be positioned to measure reflectance of mirror surface samples from the ICPC. Using this device, a map of reflector performance for the ICPC array has been generated.
Fig. 18. Third Level Reflectance Degradation. Fig. 19. Fourth Level Reflectance Degradation.
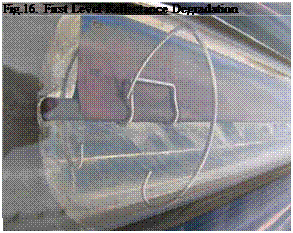
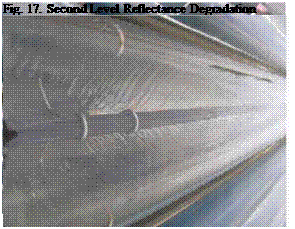
Four levels of reflectance degradation are identified for the Sacramento site. At level 1 degradation, shown in Fig. 16, the reflector still performs well with just a minor change in the reflector appearance. In level 2 degradation, shown in Fig. 17, there is some whitening of the reflector. In level 3 degradation, shown in Fig.18, there is a substantial amount of degradation of
the reflector. In level 4 degradation, shown in Fig. 19, most of reflector is gone and you can easily see through it.
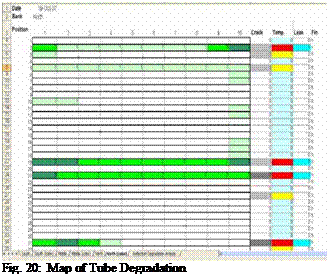
At the site, all 336 tubes were categorized, one-by-one, by their reflectivity levels, existence of a glass crack, surface temperature, water leakage, and fin orientation. Each tube was divided into ten sections along its length. Degradation levels were identified and marked for each of the ten sections. Fig. 20 shows a color mapping of tube degradation information for a portion of the array.
 |
Reflector samples representative of the four different degradation levels were taken from the Sacramento site for measurements in the laser laboratory at Colorado State University, as in Fig. 21. The samples for the four levels of degradation and undegraded reflector samples were measured for their reflectivity by the laser and detector device. Using this device, a map of reflector performance for the ICPC array is being generated. The reflectance results are shown in Table 1 for each level of degradation.
[1] Garrison, J. D., Optimization of Fixed Solar Thermal Collectors, Solar Energy, v23, 1979
[2] Snail, J. J., O’Gallagher and R. Winston, A Stationary Evacuated Collector with Integrated Concentrator, Solar Energy, v33, 1983
[3]  Winston, R, O’Gallagher, J., Mahoney, A. R., Dudley, V. E. and Hoffman, R., “Initial Performance Measurements from a Low Concentration Version of an Integrated Compound Parabolic Concentrator (ICPC)”, Proceedings of the 1999 ASES Annual Conference, Albuquerque NM, June, 1998 [5] [6]
Winston, R, O’Gallagher, J., Mahoney, A. R., Dudley, V. E. and Hoffman, R., “Initial Performance Measurements from a Low Concentration Version of an Integrated Compound Parabolic Concentrator (ICPC)”, Proceedings of the 1999 ASES Annual Conference, Albuquerque NM, June, 1998 [5] [6]
O’Gallagher, Tom Henkel and Jim Bergquam, “Performance of the Sacramento Demonstration ICPC Collector and Double Effect Chiller in 2000 and 2001”, Solar Energy, vol. 76, pages 175-180, January 2004.
[6] Duff, William, Jirachote Daosukho, Klaus Vanoli, Roland Winston, Joseph O’Gallagher, Tom Henkel and Jim Bergquam, “Comparisons of the Performance of Three Different Types of Evacuated Tubular Solar
Collectors”, American Solar Energy
Table 1: Measurement of Reflectivity S°ciety 2006 Denvei;
Colorado, July 2006.
[7] 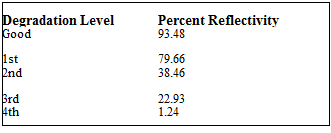 Duff, William S. and Jirachote Daosukho, “A Performance and Reliability Study of a Novel ICPC Solar Collector Installation”, American Solar Energy Society 2007 Congress, Cleveland, Ohio, July 2007.
Duff, William S. and Jirachote Daosukho, “A Performance and Reliability Study of a Novel ICPC Solar Collector Installation”, American Solar Energy Society 2007 Congress, Cleveland, Ohio, July 2007.