Solar thermal collectors and applications
Stationary collectors
Solar energy collectors are basically distinguished by their motion, i. e. stationary, single axis tracking and two - axes tracking, and the operating temperature. Initially,
Table 1
|
Solar energy collectors
|
Motion
|
Collector type
|
Absorber type
|
Concentration ratio
|
Indicative temperature range (°C)
|
|
Stationary
|
Flat plate collector (FPC)
|
Flat
|
1
|
30-80
|
|
|
Evacuated tube collector (ETC)
|
Flat
|
1
|
50-200
|
|
|
Compound parabolic collector (CPC)
|
Tubular
|
1-5
|
60-240
|
|
Single-axis tracking
|
|
|
5-15
|
60-300
|
|
|
Linear Fresnel reflector (LFR)
|
Tubular
|
10-40
|
60-250
|
|
|
Parabolic trough collector (PTC)
|
Tubular
|
15-45
|
60-300
|
|
|
Cylindrical trough collector (CTC)
|
Tubular
|
10-50
|
60-300
|
|
Two-axes tracking
|
Parabolic dish reflector (PDR)
|
Point
|
100-1000
|
100-500
|
|
|
Heliostat field collector (HFC)
|
Point
|
100-1500
|
150-2000
|
Note: Concentration ratio is defined as the aperture area divided by the receiver/absorber area of the collector.
|
|
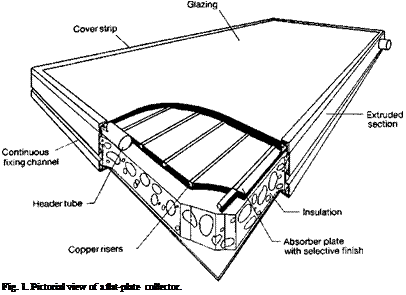
Fig. 1. Pictorial view of a flat-plate collector.
|
the stationary solar collectors are examined. These collectors are permanently fixed in position and do not track the sun. Three types of collectors fall in this category:
1. Flat plate collectors (FPC);
2. Stationary compound parabolic collectors (CPC);
3. Evacuated tube collectors (ETC).
In reality the heat loss coefficient UL in Eqs (2) and (42) is not constant but is a function of collector inlet and ambient temperatures. Therefore: TOC o "1-5" h …
The term greenhouse effect has generally been used for the role of the whole atmosphere (mainly water vapour and clouds) in keeping the surface of the earth warm. Recently however, …
Simulations are powerful tools for process design offering a number of advantages as outlined in the previous sections. However, there are limits to their use. For example, it is easy …