ERA-40 Validation
ERA-40 is a reanalysis of the global atmosphere and surface conditions for 45-years, over the period from September 1957 through August 2002 by ECMWF. Many sources of the meteorological observations were used. This data was run through the ECMWF computer model at a 40km resolution. As the ECMWF's computer model is one of the more highly-regarded in the field of forecasting, many scientists take its reanalysis to have similar merit. The data is stored in GRIB format. The reanalysis was done in an effort to improve the accuracy of historical weather maps and aid in a more detailed analysis of various weather systems through a period that was severely lacking in computerized data. With the data from reanalyses such as this, many of the more modern computerized tools for analyzing
storm systems can be utilized, at least in part, because of this access to a computerized simulation of the atmospheric state.
The period of data studied goes from 1994 to 2004 and the variable studied is downward global solar radiation. The resolution of the dataset is 1° or 100km.
Accuracy of each one of the models presented is studied in terms of Root Mean Squared Deviation (RMSD):
being N the population size, O the variable observed and O* predicted variable.
 |
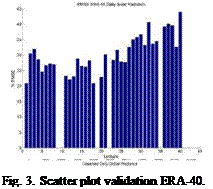 |
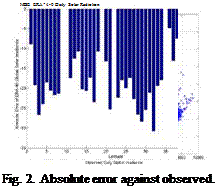
The validation is done comparing with ground measurements from 40 stations from AEMet. Results from validation can be show in Figs. 2-5. . The graphic shows all the stations ordered from lower latitude to higher latitude. Overall data is underestimated for high solar radiation values and Normalized RMSD goes from 20% to 45% and the error gets increased with the latitude.