Description of the test set-up
As mentioned above, the experience gathered during the various central receiver technology projects 7 8 9 and materials treatment activities carried out in the PSA’s Solar Furnace1,2 have been combined in the design of the test assembly. Figure 2# below is a diagram of the main system components.
Air is blown through the ceramic absorber of the solar receiver where it is heated, supplying the energy source for an industrial, high-temperature process in the ‘treatment chamber’. The ‘treatment chamber’, which is right behind the absorber, is the main innovation with respect to a conventional volumetric receiver system.
A blower forces the air into the system and regulates the air temperature through speed variation. The air passes through the whole system, from the receiver to the blower. There is an auxiliary fresh air inlet just at the blower entrance, regulated with a by-pass valve, so the temperature of the air passing through is below 200°C which is the maximum allowed for the blower.
Fig. 2. Schematic view of the device and the air circuit
The receiver temperature can be controlled with the opening percentage of the Solar Furnace’s flux shutter.
The operator of the system is able to control both the blower speed and the aperture of the shutter on-line from the control room. The next step would be to implement an automatic control loop, able to handle both variables in order to make the reference temperature to follow a desired T-t profile.
The receiver has a 30 cm diameter to fit in the solar furnace focus. The main focus characteristics are shown in Figure 3 below.
![]() Power information on Solar Furnace Target
Power information on Solar Furnace Target
Total Power................................. = 68 kV
Peak oflrradiance....................... = 3029 kW/nf
Statistic analysis ol Irradiance distribution:
Slant Ranee................................. = 7.445 m
Centroid location....................... = (0.013,-0.012) m
Peak location.............................. = (0.016,-0.017) m
90-Percent Energy Radius........ = 0.132 m
Maximum rms-radtus............... = 0.063 m
Minimum rms-radius................. = 0.058 m
 ......... = 1.08
......... = 1.08
Elhpticity direction..................... = 183.6 deg
rim.
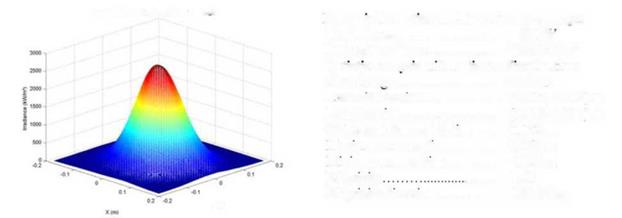 Fig. 3. Flux map in the PSA’s Solar Furnace
Fig. 3. Flux map in the PSA’s Solar Furnace