Data transformation
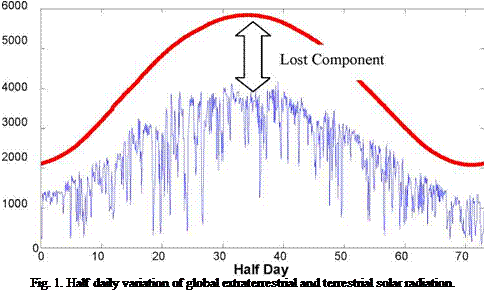
In this study the generation of the variable which is going to be used to forecast future values of half daily solar global radiation is done taking into account gaussian and stationary properties needed in the time series to be used by predictive methods. This approach is based on “lost solar component” (Fig.
1.) defined previously.
Lost component time series presents higher variation in central months of the year due to higher solar radiation levels and bigger influence of cloudiness reflection and absorption on solar irradiance.
Elimination of the trend component is done differencing between successive time steps of lost component time series.
 W/m2 half day
W/m2 half day
 |
In the other side, synoptic predictions of future states of sky conditions by statistical post-processing models presents less uncertainty than direct output of global solar irradiance in numerical weather prediction models. The classification of sky conditions is done by national weather services in six levels Fig. 2. As sky condition variable wasn’t available directly from AEMet it has been simulated dividing measured solar radiation in six levels. Future variation of sky conditions is combined with the difference of lost component time series as input to predictive methods. Besides, pure statistical models have the advantage of limiting the upper error of prediction and improving predictions errors of persistence by making relations of patterns of past observations and future values. In the next sections, results of using and not using sky condition as input to neural network is shown.